In this article, we will explore how you can integrate Python’s folium library into a Node.js backend application using Javonet. This setup allows you to leverage Python’s powerful libraries for geospatial data and map creation while using Node.js as the server-side framework.
Why Use Python’s folium for Interactive Maps?
- Ease of Use: Python’s
folium allows you to create beautiful, interactive maps with minimal effort.
- Advanced Features: You can easily create heatmaps, clusters, popups, and more.
- Powerful Data Integration: Python integrates seamlessly with data science libraries like
geopandas, making it ideal for geospatial analysis.
Scenario: Creating an Enhanced Map
Imagine you are building a logistics system, and you want to display key distribution centers on an interactive map. Python’s folium makes it easy to achieve this, and Javonet allows you to execute Python code within a Node.js environment.
Step 0: Install Dependencies
Before we start, ensure you have the necessary dependencies installed.
-
Install Python dependencies for generating the map:
-
Install Node.js dependencies for using Javonet and Express:
npm init -y
npm install javonet-nodejs-sdk express
Step 1: Create the Map with Python
First, let’s write the Python script to generate a map using folium.
map.py
import folium
from folium.plugins import HeatMap, MarkerCluster
import random
def generate_random_points(center, num_points, spread=0.1):
"""Generate random points around a center location."""
return [
{
"lat": center["lat"] + random.uniform(-spread, spread),
"lon": center["lon"] + random.uniform(-spread, spread),
"popup": f"Random point {i}"
}
for i in range(num_points)
]
def create_enhanced_map():
center_lat = 37.7749
center_lon = -122.4194
m = folium.Map(
location=[center_lat, center_lon],
zoom_start=6,
tiles="CartoDB Positron"
)
main_locations = [
{"lat": 37.7749, "lon": -122.4194, "name": "San Francisco", "popup": "This is San Francisco!"},
{"lat": 34.0522, "lon": -118.2437, "name": "Los Angeles", "popup": "This is Los Angeles!"},
{"lat": 40.7128, "lon": -74.0060, "name": "New York", "popup": "This is New York!"}
]
additional_points = []
for loc in main_locations:
additional_points.extend(generate_random_points(loc, 33))
all_locations = main_locations + additional_points
heat_data = [[loc["lat"], loc["lon"]] for loc in all_locations]
HeatMap(heat_data, radius=25, blur=15).add_to(m)
marker_cluster = MarkerCluster().add_to(m)
for loc in all_locations:
folium.Marker(
location=[loc["lat"], loc["lon"]],
popup=loc["popup"],
icon=folium.Icon(icon="info-sign")
).add_to(marker_cluster)
folium.LayerControl().add_to(m)
map_file = "enhanced_map.html"
m.save(map_file)
return map_file
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("Map saved to:", create_enhanced_map())
This Python script generates a map centered on California with markers for San Francisco, Los Angeles, and New York, as well as a heatmap and random points scattered around these cities.
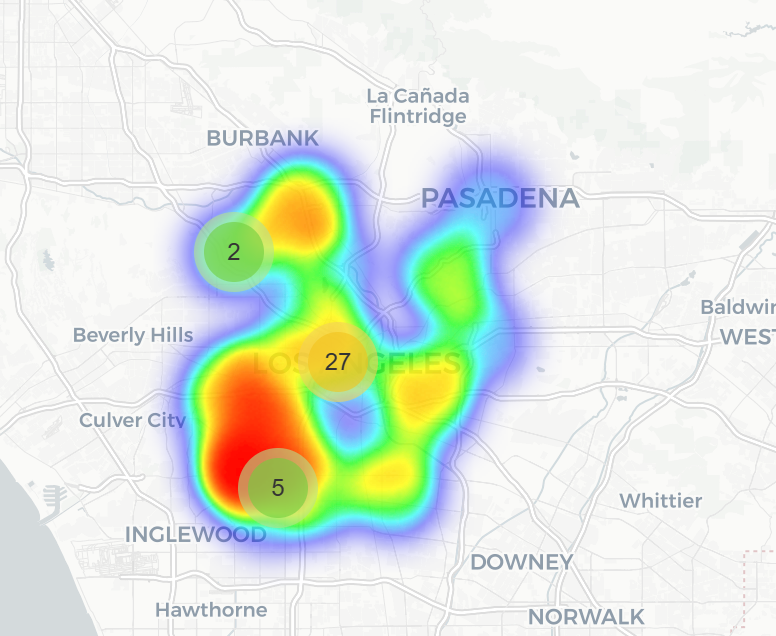
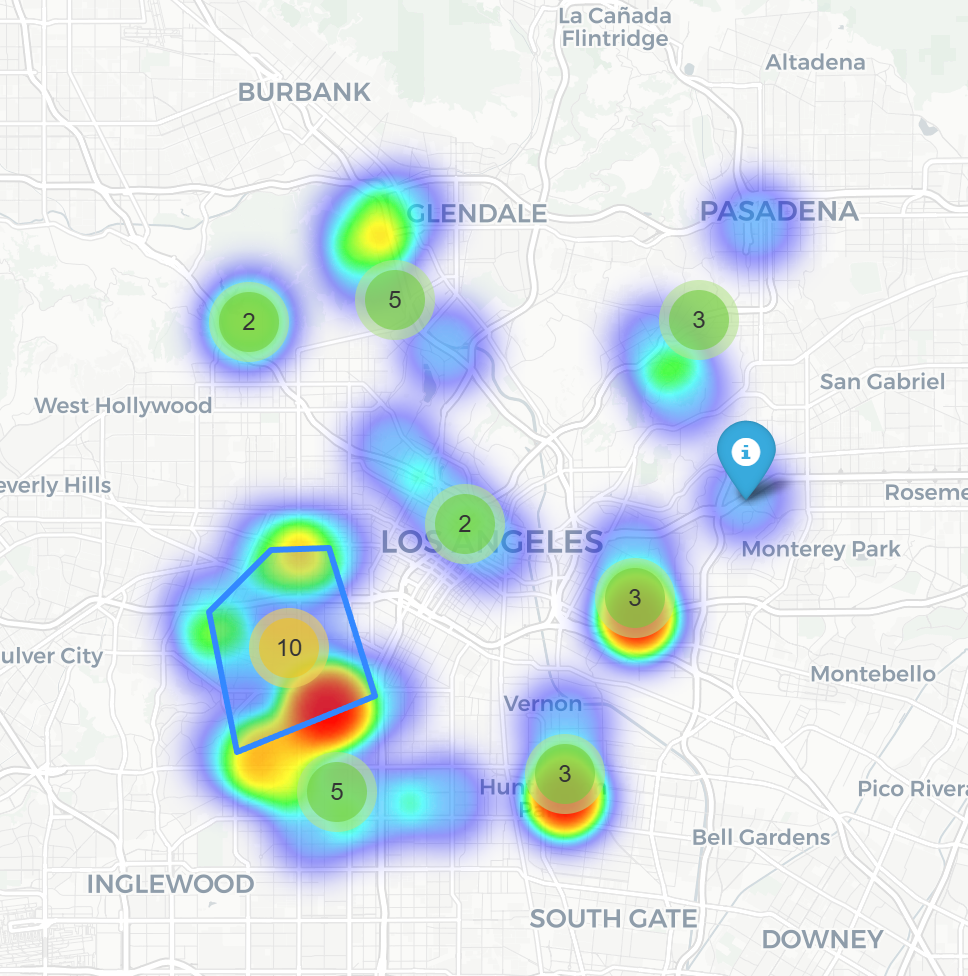
Now we need to just call our Python code in Node.js. We can do it by running our ready python script inside Node.js App (Option 1) or we can write Python code nativly (Option 2) in our app thanks to Javonet
Step 2 (Option 1): Run the Python Script from Node.js Using Javonet
Now that the Python script is ready, let’s integrate it into your Node.js application using Javonet.
app.js
const express = require('express');
const path = require('path');
const { Javonet } = require('javonet-nodejs-sdk');
const app = express();
const port = 3001;
Javonet.activate("key");
let calledRuntime = Javonet.inMemory().python();
const libraryPath = ".";
calledRuntime.loadLibrary(libraryPath);
async function generateMap() {
try {
let pythonScriptType = calledRuntime.getType('map');
let response = pythonScriptType.invokeStaticMethod('create_enhanced_map').execute();
let mapFilePath = response.getValue();
console.log("Map generated successfully:", mapFilePath);
return mapFilePath;
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error running the Python script:", error);
return null;
}
}
app.get('/', async (req, res) => {
const mapFilePath = await generateMap();
if (mapFilePath) {
res.sendFile(path.join(__dirname, mapFilePath));
} else {
res.status(500).send("Error generating the map.");
}
});
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Server is running at http://localhost:${port}`);
});
Step 2 (Option 2): Write Python code in Node.js Using Javonet
To make things easier i wrote simple version of our Python code right here:
import folium
location = [37.7749, -122.4194]
m = folium.Map(location)
marker = folium.Marker(location, "San Francisco")
m.add_child(marker)
m.save("simple_map.html")
So now we can nativly use Python Code in Node app!
const { Javonet } = require('javonet-nodejs-sdk');
Javonet.activate("javonet-key");
let calledRuntime = Javonet.inMemory().python();
const libraryPath = ".";
calledRuntime.loadLibrary(libraryPath);
let folium = calledRuntime.getType('folium').execute()
const location = [37.7749, -122.4194]
let map = folium.invokeStaticMethod("Map", location).execute()
let marker = folium.invokeStaticMethod("Marker", location, "San Francisco").execute()
map.invokeStaticMethod("add_child", marker).execute()
map.invokeStaticMethod("save", "simple.html").execute()
This code will generate simple map with Python in Node.Js!
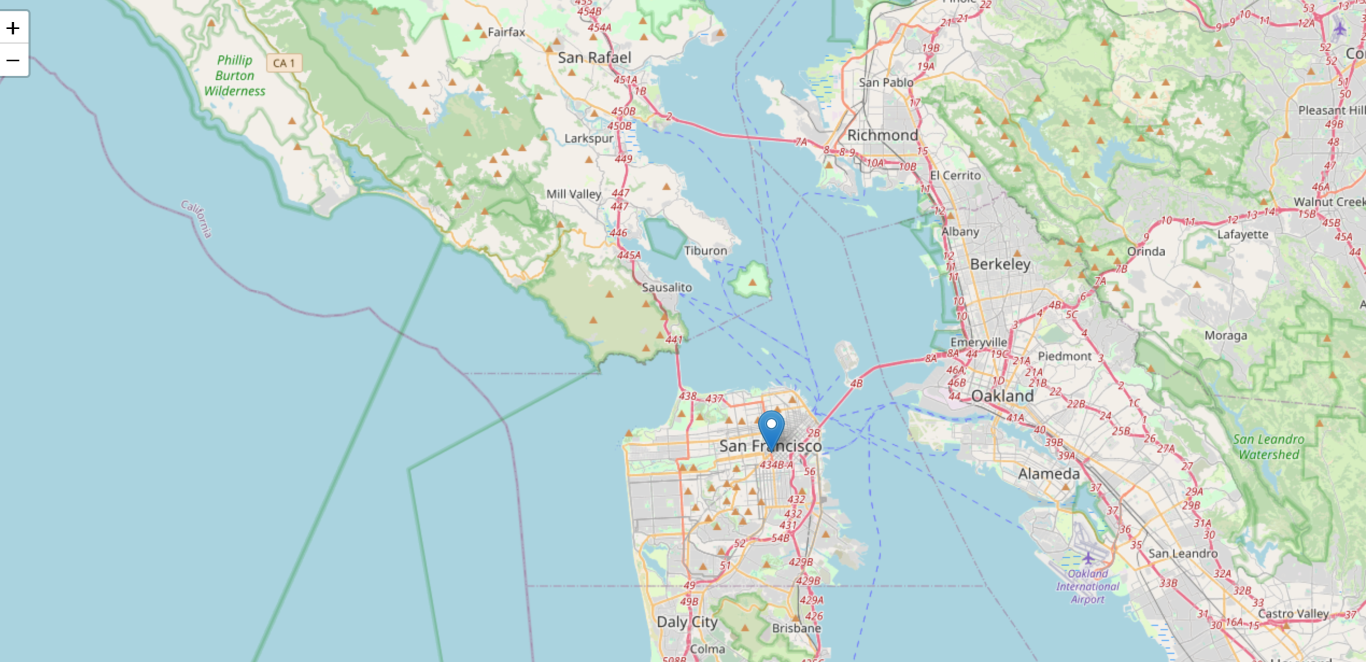
Step 3: Test the Node.js Application
-
Start the Node.js server:
-
Access the map: Visit http://localhost:3001 in your web browser to see the interactive map generated by the Python script.
Here are some examples:
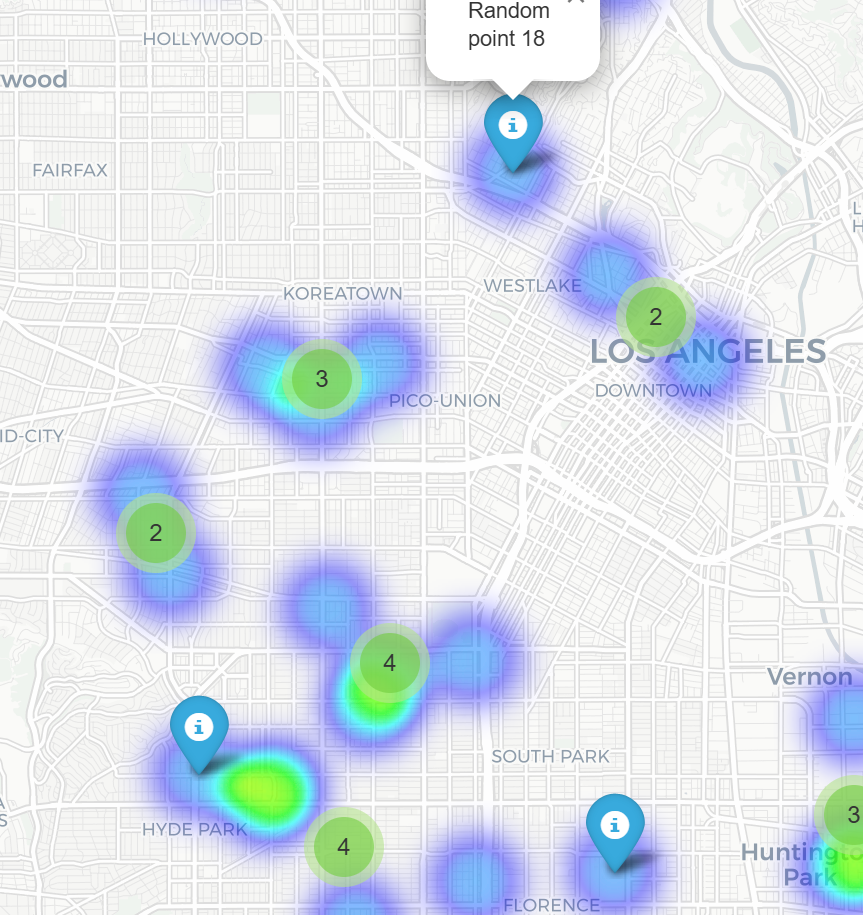
Where to use it?
You can use this functionality to build a custom Node.js app that, with a click (or based on some data), will generate beautiful maps that you can easily interact with :) That’s another example of Javonet usage! Feel free to share your ideas about cross-language integrations!
Directory Structure
Your project directory should look like this:
/maps
├── map.py // Python script to generate the map (if option 2 without map.py)
├── app.js // Node.js backend using Javonet
Conclusion
By using Javonet to integrate Python’s folium library into your Node.js application, you can easily generate advanced interactive maps in Python and serve them through your Node.js backend. This approach leverages the strengths of both ecosystems, enabling powerful geospatial data handling with Python and fast web service delivery with Node.js.
Feel free to experiment with different map types and Python libraries to extend your application further!
In this article, we will explore how you can integrate Python’s
foliumlibrary into a Node.js backend application using Javonet. This setup allows you to leverage Python’s powerful libraries for geospatial data and map creation while using Node.js as the server-side framework.Why Use Python’s
foliumfor Interactive Maps?foliumallows you to create beautiful, interactive maps with minimal effort.geopandas, making it ideal for geospatial analysis.Scenario: Creating an Enhanced Map
Imagine you are building a logistics system, and you want to display key distribution centers on an interactive map. Python’s
foliummakes it easy to achieve this, and Javonet allows you to execute Python code within a Node.js environment.Step 0: Install Dependencies
Before we start, ensure you have the necessary dependencies installed.
Install Python dependencies for generating the map:
Install Node.js dependencies for using Javonet and Express:
Step 1: Create the Map with Python
First, let’s write the Python script to generate a map using
folium.map.py
import folium from folium.plugins import HeatMap, MarkerCluster import random def generate_random_points(center, num_points, spread=0.1): """Generate random points around a center location.""" return [ { "lat": center["lat"] + random.uniform(-spread, spread), "lon": center["lon"] + random.uniform(-spread, spread), "popup": f"Random point {i}" } for i in range(num_points) ] def create_enhanced_map(): # Define the center of the map center_lat = 37.7749 center_lon = -122.4194 # Create a map object with CartoDB Positron tiles m = folium.Map( location=[center_lat, center_lon], zoom_start=6, tiles="CartoDB Positron" ) # Main locations for the heatmap and markers main_locations = [ {"lat": 37.7749, "lon": -122.4194, "name": "San Francisco", "popup": "This is San Francisco!"}, {"lat": 34.0522, "lon": -118.2437, "name": "Los Angeles", "popup": "This is Los Angeles!"}, {"lat": 40.7128, "lon": -74.0060, "name": "New York", "popup": "This is New York!"} ] # Generate additional random points around the main locations additional_points = [] for loc in main_locations: additional_points.extend(generate_random_points(loc, 33)) # Combine main locations and additional points all_locations = main_locations + additional_points # Add a heatmap with enhanced parameters heat_data = [[loc["lat"], loc["lon"]] for loc in all_locations] HeatMap(heat_data, radius=25, blur=15).add_to(m) # Add markers with popups marker_cluster = MarkerCluster().add_to(m) for loc in all_locations: folium.Marker( location=[loc["lat"], loc["lon"]], popup=loc["popup"], icon=folium.Icon(icon="info-sign") ).add_to(marker_cluster) # Add layer control folium.LayerControl().add_to(m) # Save the map as an HTML file map_file = "enhanced_map.html" m.save(map_file) return map_file # Example usage if __name__ == "__main__": print("Map saved to:", create_enhanced_map())This Python script generates a map centered on California with markers for San Francisco, Los Angeles, and New York, as well as a heatmap and random points scattered around these cities.
Now we need to just call our Python code in Node.js. We can do it by running our ready python script inside Node.js App (Option 1) or we can write Python code nativly (Option 2) in our app thanks to Javonet
Step 2 (Option 1): Run the Python Script from Node.js Using Javonet
Now that the Python script is ready, let’s integrate it into your Node.js application using Javonet.
app.js
Step 2 (Option 2): Write Python code in Node.js Using Javonet
To make things easier i wrote simple version of our Python code right here:
import folium location = [37.7749, -122.4194] m = folium.Map(location) marker = folium.Marker(location, "San Francisco") m.add_child(marker) m.save("simple_map.html")So now we can nativly use Python Code in Node app!
This code will generate simple map with Python in Node.Js!

Step 3: Test the Node.js Application
Start the Node.js server:
Access the map: Visit
http://localhost:3001in your web browser to see the interactive map generated by the Python script.Here are some examples:

Where to use it?
You can use this functionality to build a custom Node.js app that, with a click (or based on some data), will generate beautiful maps that you can easily interact with :) That’s another example of Javonet usage! Feel free to share your ideas about cross-language integrations!
Directory Structure
Your project directory should look like this:
Conclusion
By using Javonet to integrate Python’s
foliumlibrary into your Node.js application, you can easily generate advanced interactive maps in Python and serve them through your Node.js backend. This approach leverages the strengths of both ecosystems, enabling powerful geospatial data handling with Python and fast web service delivery with Node.js.Feel free to experiment with different map types and Python libraries to extend your application further!